In the evolving landscape of law enforcement, data has become an invaluable tool for solving and preventing criminal activity. Crime analysis, a field at the intersection of data science and policing, leverages information to uncover patterns, trends, and potential threats. This article delves into the crucial role of data in modern law enforcement, shedding light on how it aids in the resolution and prevention of criminal incidents.
**1. Unraveling Crime Analysis: A Comprehensive Overview
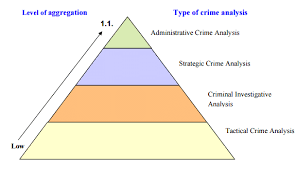
a. Defining Crime Analysis: An in-depth exploration of crime analysis, encompassing its objectives, methodologies, and the vital role it plays in law enforcement.
b. Data Sources in Crime Analysis: An examination of the diverse data sources that form the foundation of crime analysis, ranging from incident reports to demographic information.
**2. Solving Crimes Through Data-Driven Policing
a. Pattern Recognition and Crime Solvability: How data analysis helps identify recurring patterns in criminal behavior, aiding in the apprehension of suspects and resolution of cases.
b. Cold Case Resolutions: Real-life examples showcasing instances where cold cases have been reopened and solved through the application of advanced data analysis techniques.
**3. The Power of Crime Mapping
a. Spatial Analysis in Law Enforcement: Exploring the use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in crime mapping, which provides invaluable insights into crime hotspots and trends.
b. Predictive Policing: How data-driven models forecast potential crime locations, allowing law enforcement agencies to allocate resources strategically and proactively prevent criminal activity.
**4. Targeted Interventions for Crime Prevention
a. Identifying At-Risk Areas: Case studies demonstrating how data-driven approaches help pinpoint neighborhoods or regions susceptible to criminal activity, enabling focused intervention efforts.
b. Community Engagement and Policing: The role of data in fostering collaboration between law enforcement and communities, enhancing trust, and collectively working towards crime prevention.
**5. Reducing Recidivism Through Data-Backed Strategies
a. Risk Assessment Tools: The application of data-driven risk assessment tools to evaluate the likelihood of reoffending, allowing for tailored intervention and rehabilitation programs.
b. Effective Resource Allocation: How data analysis informs the allocation of resources towards rehabilitation and support programs, optimizing efforts to reduce recidivism rates.
**6. Data Privacy and Ethical Considerations
a. Balancing Privacy and Public Safety: Addressing the ethical implications of data-driven policing, including concerns related to privacy, transparency, and accountability.
b. Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: The importance of robust legal and regulatory frameworks to ensure that data-driven policing adheres to established standards and danatoto safeguards.
Conclusion: A Data-Driven Future for Law Enforcement
Crime analysis stands at the forefront of a new era in law enforcement, where data-driven approaches are reshaping how criminal activity is addressed. By leveraging the power of information, law enforcement agencies are not only solving crimes more effectively but also proactively preventing them. The integration of data-driven strategies, combined with community engagement and ethical considerations, paves the way for safer, more secure communities. As technology continues to advance, the role of data in law enforcement will only become more central, marking a significant step forward in the pursuit of public safety and justice.