List Of Contents
Concept design serves as the foundation of many creative industries, including architecture, product development, digital media, and entertainment. It is a crucial stage in the design process where abstract ideas take form and are refined into feasible concepts. By blending creativity and functionality, concept design lays the groundwork for successful projects. This article explores the importance, process, and challenges of concept, emphasizing its role in shaping innovative solutions.
Understanding Concept Design

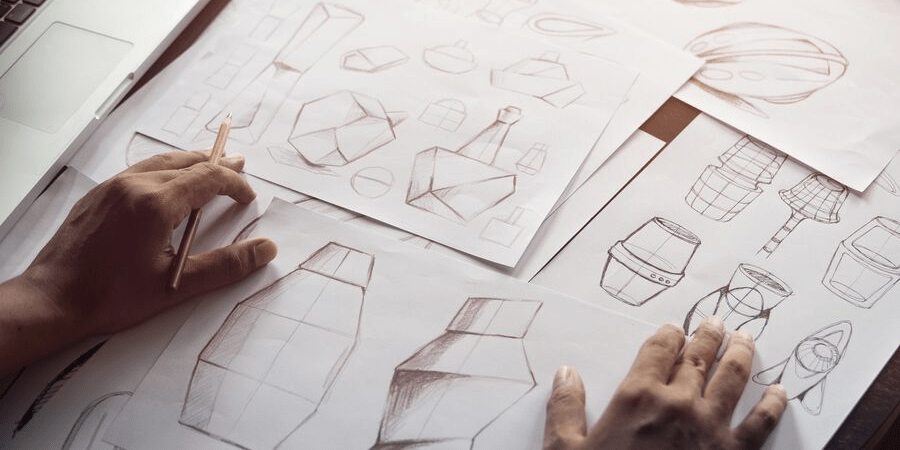
Concept design is the initial phase of any creative project, focusing on generating and developing ideas. It aims to address specific needs, solve problems, or create opportunities. This stage typically involves brainstorming, sketching, modeling, and other creative activities that translate abstract concepts into tangible outcomes. The key objective is to explore possibilities without being constrained by technical or logistical limitations.
Concept design is not about creating the final product but establishing a vision that guides subsequent development. It bridges the gap between imagination and execution, enabling designers to explore ideas before committing to a specific direction.
The Importance of Concept Design
Concept design plays a pivotal role in the success of any project. Its significance can be understood through several key aspects:
- Clarifying Objectives: Concept helps stakeholders define the goals and purpose of a project. By understanding the needs and expectations, designers can align their creative efforts with the desired outcomes.
- Encouraging Innovation: This phase fosters creativity and experimentation, encouraging out-of-the-box thinking. By exploring various possibilities, designers can discover unique solutions that set their projects apart.
- Minimizing Risks: Investing time in concept design reduces the risk of costly mistakes later in the process. It allows for identifying potential challenges and addressing them before they escalate.
- Improving Communication: Concept facilitates collaboration among team members and stakeholders. Visual representations of ideas make it easier to convey concepts, gather feedback, and ensure everyone is on the same page.
The Process of Concept Design
The concept design process involves several iterative steps, each contributing to the refinement of ideas. While the specifics may vary depending on the industry or project, the core stages are as follows:
Research and Analysis
Every concept design begins with research. Designers gather information about the project’s context, target audience, market trends, and technical requirements. This step ensures that the design is grounded in reality and addresses relevant needs.
Ideation
Ideation is the creative heart of concept. Designers brainstorm and generate multiple ideas, often using techniques such as mind mapping, sketching, or mood boards. This stage encourages experimentation and the exploration of diverse possibilities.
Concept Development
Once promising ideas are identified, designers begin refining them into more structured concepts. This phase often involves creating prototypes, digital models, or mockups to visualize the ideas and assess their feasibility.
Feedback and Iteration
Feedback is integral to the concept design process. Designers present their concepts to stakeholders or team members, gather input, and refine their designs based on the feedback received. This iterative approach ensures that the final concept aligns with project objectives.
Final Presentation
The concept design process culminates in a comprehensive presentation. Designers showcase their refined concepts using visual aids such as renderings, videos, or prototypes. This presentation serves as the blueprint for the next stages of development.
Tools and Techniques in Concept Design

Concept design relies on a variety of tools and techniques to bring ideas to life. Modern technology has expanded the possibilities, offering designers powerful tools to enhance their creativity and efficiency. Key tools and techniques include:
- Sketching and Drawing: Traditional sketching remains a cornerstone of concept. It allows designers to quickly visualize ideas and explore variations.
- 3D Modeling Software: Tools like Blender, Rhino, or SketchUp enable designers to create realistic digital models. These models are invaluable for visualizing spatial relationships and testing design feasibility.
- Prototyping: Prototypes, whether physical or digital, help designers test and refine their ideas. They provide tangible representations of concepts, enabling better evaluation and feedback.
- Rendering and Visualization: High-quality renderings create realistic depictions of concepts, making it easier to communicate ideas to stakeholders.
- Collaborative Platforms: Tools like Miro or Figma facilitate collaboration among team members, enabling real-time feedback and seamless sharing of ideas.
Challenges in Concept Design
While concept design is a vital part of the creative process, it is not without challenges. Designers often face obstacles that can hinder progress and impact the quality of their work:
- Balancing Creativity and Feasibility: Striking the right balance between innovative ideas and practical constraints can be difficult. Designers must ensure their concepts are both imaginative and achievable.
- Time Constraints: Concept often operates under tight deadlines, limiting the time available for exploration and refinement.
- Communication Gaps: Miscommunication among team members or stakeholders can lead to misunderstandings and misaligned expectations.
- Adapting to Feedback: Incorporating feedback effectively requires flexibility and resilience. Designers must remain open to criticism while staying true to their vision.
The Role of Concept Design in Different Industries
Concept design is a versatile process that adapts to the unique needs of various industries. Its application varies across fields, but the core principles remain consistent:
Architecture
In architecture, concept design focuses on creating initial building layouts and exploring structural possibilities. Architects use sketches, physical models, and 3D software to present their vision.
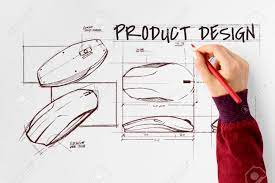
Product Design
For product designers, concept involves ideating and refining ideas for new products. This stage emphasizes user needs, aesthetics, and functionality.
Film and Entertainment
In the entertainment industry, concept design is critical for visual storytelling. Designers create character concepts, environments, and props that shape the look and feel of films, games, or animations.
Digital Media
Concept design in digital media involves creating user interfaces, branding materials, and multimedia content. It prioritizes usability and visual appeal to enhance user experiences.
The Future of Concept Design
As technology continues to advance, the field of concept design is evolving rapidly. Emerging mariatogel trends are shaping how designers approach their work and the tools they use:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered tools are transforming concept by automating repetitive tasks and providing intelligent suggestions. This allows designers to focus on creativity and innovation.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: VR and AR technologies enable designers to immerse themselves in their concepts, offering new ways to visualize and test ideas.
- Sustainable Design: With growing awareness of environmental issues, concept is increasingly emphasizing sustainability. Designers are exploring eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce their projects’ impact on the planet.
- Collaboration Across Disciplines: The integration of diverse expertise is becoming essential in concept design. Cross-disciplinary collaboration enriches the creative process and leads to more holistic solutions.
Conclusion
Concept design is a dynamic and essential phase in the creative process, bridging the gap between imagination and execution. It empowers designers to explore possibilities, refine ideas, and create innovative solutions that meet real-world needs. By understanding the principles and embracing the challenges of concept design, professionals across industries can harness its potential to drive success and innovation. With advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on sustainability, the future of concept holds exciting possibilities for shaping the world around us.