List Of Contents
- 0.1 1. Understanding Complex Systems
- 0.2 2. The Fundamentals of Network Theory
- 0.3 3. Applications in Social Networks
- 0.4 4. Biological Networks: Unraveling Life’s Interconnectedness
- 0.5 5. Technological Networks: From the Internet to Transportation
- 0.6 6. Node Centrality: Identifying Key Players
- 0.7 7. Connectivity Patterns: Clusters, Hubs, and Bridges
- 0.8 8. Network Visualization: Bringing Structures to Life
- 0.9 9. Dynamics of Networks: Change and Adaptation
- 0.10 10. Resilience and Robustness: Navigating Network Failures
- 0.11 11. Ethical Considerations in Network Analysis
- 0.12 In Conclusion: Illuminating Complex Systems
- 1 Author
Network analysis is a dynamic field that provides invaluable insights into the structures and connections within complex systems. It employs graph theory and visualization techniques to uncover patterns, relationships, and behaviors within networks. This article is a comprehensive exploration of network analysis, shedding light on its principles, applications across diverse domains, and the methods used to map and analyze connections within intricate systems.
1. Understanding Complex Systems
Explore the concept of complex systems and how they are modeled as networks to better understand their underlying structures and behaviors.
2. The Fundamentals of Network Theory
Dive into the foundational principles of network theory, including nodes, edges, and various metrics used to quantify network properties.
Discover how network analysis is applied to understand social interactions, influence dynamics, and information dissemination in online and offline communities.
4. Biological Networks: Unraveling Life’s Interconnectedness
Explore the application of network analysis in biology, from protein-protein interaction networks to neural connectivity in the brain.
5. Technological Networks: From the Internet to Transportation
Examine how network analysis is used to study and optimize various technological systems, such as the internet, transportation networks, and communication infrastructures.
6. Node Centrality: Identifying Key Players
Learn about measures of node centrality, which identify the most influential or central nodes within a network.
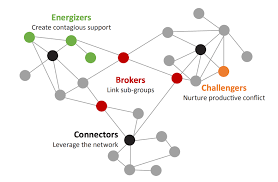
7. Connectivity Patterns: Clusters, Hubs, and Bridges
Discover different network motifs and patterns, such as cliques, hubs, and bridges, that shape the flow of information or resources in a network.
8. Network Visualization: Bringing Structures to Life
Explore the visual representation of networks, which provides powerful insights into their structures and connectivity.
9. Dynamics of Networks: Change and Adaptation
Understand how networks evolve over time, whether through the addition or removal of nodes and edges, or changes in their attributes.
Learn about strategies to enhance the resilience of networks against failures, attacks, or disruptions.
11. Ethical Considerations in Network Analysis
Discuss the ethical implications of network analysis, particularly in areas like privacy, security, and informed consent.
In Conclusion: Illuminating Complex Systems
Network analysis is a versatile tool that unravels the intricate relationships within complex systems, providing valuable insights across various disciplines. By understanding the principles and applications of network theory, we gain a powerful tool for navigating the complexities of our interconnected world.
In Conclusion:
Network analysis is a versatile tool that unravels the intricate relationships within complex systems, providing valuable insights across various disciplines. By understanding the principles and applications of network theory, we gain a powerful tool for navigating the complexities of our interconnected world.