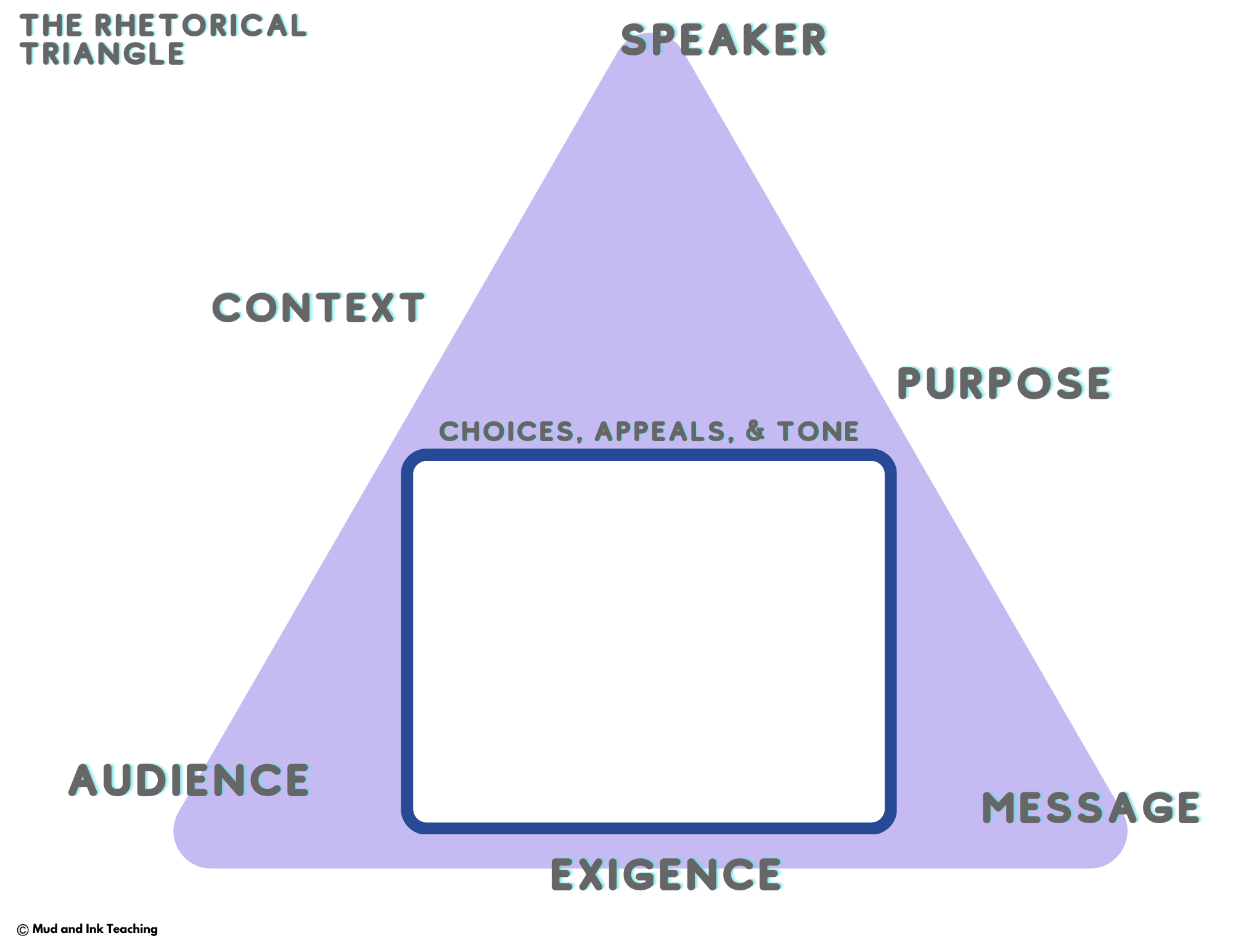
In the realm of communication, the ability to persuade is a powerful tool. Rhetorical analysis is a method of examining the techniques and strategies employed by speakers and writers to effectively influence their audience. By understanding the elements of persuasion, we can gain insight into how influential messages are crafted and delivered. In this article, we will delve into the world of rhetorical analysis, decoding the power of persuasion and the key components that make it effective.
1. Understanding Rhetorical Analysis: Rhetorical analysis is the examination of how language and communication techniques are used to persuade an audience. It involves dissecting the elements of a message, such as the use of language, structure, and rhetorical devices, to uncover the strategies employed by the speaker or writer.
2. Ethos, Pathos, Logos: The Three Pillars of Persuasion: Ethos, pathos, and logos are the fundamental appeals used in persuasive communication. Ethos establishes the speaker’s credibility and authority. Pathos appeals to the emotions and values of the audience. Logos relies on logical reasoning and evidence. Effective persuasion often incorporates a combination of these appeals to create a compelling argument.
3. Analyzing Rhetorical Devices: Rhetorical devices are techniques used to enhance the effectiveness of communication. These include metaphors, similes, analogies, hyperbole, and rhetorical questions. By employing these devices, speakers and writers can create vivid imagery, evoke emotions, and emphasize key points.
4. Identifying Persuasive Techniques: Persuasion involves a range of techniques aimed at influencing the audience’s perception and response. These may include repetition for emphasis, the use of anecdotes to connect on a personal level, and the strategic placement of key arguments for maximum impact.
5. Deconstructing Persuasive Speeches: Analyzing famous speeches provides valuable insights into the art of persuasion. By examining speeches from historical figures like Martin Luther King Jr., Winston Churchill, and others, we can discern how they employed rhetorical devices, appeals, and effective communication strategies to inspire and mobilize audiences.
6. Recognizing Rhetorical Appeals in Written Texts: Rhetorical appeals are not limited to spoken words; they are equally vital in written communication. By scrutinizing influential written works, we can uncover how authors employ ethos, pathos, and logos to engage readers and convey their message persuasively.
7. Strategies for Effective Persuasive Writing: In written communication, employing persuasive writing strategies is paramount. This may involve crafting a compelling thesis statement, providing credible evidence, and structuring arguments in a logical and coherent manner. Additionally, using persuasive language and tone can further enhance the impact of the message.
8. Critical Thinking in Rhetoric: Engaging in rhetorical analysis requires critical thinking skills. It involves evaluating the effectiveness of persuasive techniques, considering the intended audience, and assessing the overall impact of the message. This analytical approach enables individuals to discern between well-constructed arguments and manipulative tactics.
9. Applying Rhetorical Analysis in Everyday Communication: The principles of rhetorical analysis are not confined to formal speeches or written texts. They are applicable in everyday communication scenarios, from persuasive emails and presentations to discussions and debates. Understanding how persuasion works empowers individuals to communicate more effectively and influence opinions positively.
10. The Ethical Dimension of Persuasion: While rhetoric is a powerful tool, it also carries an ethical responsibility. Persuasion should be used responsibly and ethically, with consideration for the well-being and autonomy of the audience. Recognizing the ethical implications of persuasive communication is an integral aspect of effective danatoto rhetoric.
In Conclusion,
Rhetorical analysis provides a window into the art of persuasion, revealing the techniques and strategies that shape influential messages. By understanding the interplay of ethos, pathos, and logos, recognizing rhetorical devices, and employing critical thinking, individuals can enhance their own communication skills. Whether in formal speeches, written texts, or everyday conversations, the principles of rhetorical analysis empower us to communicate more effectively and ethically, ultimately leading to more meaningful connections and impactful messages.